Catalytic converters play a crucial role in our modern society, silently working to reduce harmful emissions from vehicles and protect our environment. However, like any mechanical component, these remarkable devices are not immune to wear and tear. Have you ever wondered how catalytic converters go bad? In this article, we will delve into the inner workings of these essential automotive components, explore the common causes of their deterioration, and discuss the signs that indicate a failing catalytic converter. So, fasten your seatbelt and prepare to embark on a journey through the fascinating world of catalytic converters.
Imagine driving down a bustling city street, the hum of traffic filling the air, and suddenly, an acrid smell assaults your senses. It could be the unmistakable stench of a failing catalytic converter. While these devices are designed to last for hundreds of thousands of miles, various factors can contribute to their premature demise. The intricate network of precious metals housed within the catalytic converter can become contaminated, clogged, or damaged over time, resulting in inefficient pollutant conversion. From engine misfires and oil or coolant leaks to fuel additives and poor maintenance practices, numerous culprits can accelerate the degradation of this vital emission control device. Join us as we unravel the mysteries behind the degradation process and learn how to identify the symptoms of a failing catalytic converter before it’s too late.
How do catalytic converters go bad?
Catalytic converters can go bad due to various reasons such as engine misfires, fuel contamination, overheating, or internal damage. Symptoms of a bad catalytic converter include decreased engine performance, increased emissions, and the illumination of the “Check Engine” light. To determine if your catalytic converter is failing, it is recommended to have it inspected by a qualified mechanic.
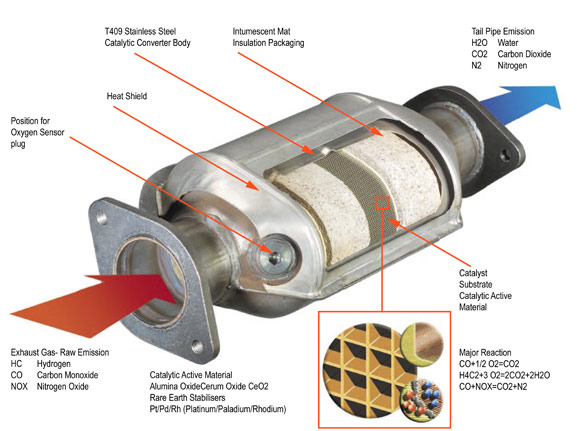
How Do Catalytic Converters Go Bad
A catalytic converter is an essential component of a vehicle’s exhaust system, responsible for reducing harmful emissions and converting them into less harmful substances. Over time, however, catalytic converters can go bad due to various reasons, causing them to lose their effectiveness. In this article, we will explore the common causes of catalytic converter failure and how to identify the signs of a failing catalytic converter.
1. Contamination from Engine Oil or Coolant
One of the main reasons why catalytic converters go bad is contamination from engine oil or coolant. Engine oil or coolant leaks can find their way into the exhaust system and coat the surface of the catalytic converter, inhibiting its ability to carry out the necessary chemical reactions. This contamination can lead to a decrease in catalytic converter efficiency and eventually result in its failure.
To prevent this type of contamination, it is important to regularly check for and address any engine oil or coolant leaks. Timely repairs and maintenance can help prolong the life of the catalytic converter and ensure it functions optimally.
2. Physical Damage
Catalytic converters can also go bad due to physical damage caused by external factors. Road debris, such as rocks or other objects, can strike the catalytic converter, causing dents or punctures. Additionally, driving over speed bumps, potholes, or other rough terrain can cause the exhaust system to experience excessive vibrations, leading to damage to the catalytic converter.
To minimize the risk of physical damage, it is important to drive cautiously and avoid rough roads whenever possible. Regular inspections of the exhaust system can also help identify any signs of physical damage early on, allowing for prompt repairs or replacement if necessary.
3. Overheating
Excessive heat can also contribute to catalytic converter failure. Over time, exposure to high temperatures can cause the internal components of the catalytic converter to deteriorate, leading to reduced efficiency or complete failure. Overheating can be caused by a variety of factors, including engine misfires, a malfunctioning oxygen sensor, or a rich fuel mixture.
Proper maintenance, such as regular tune-ups and addressing any engine problems promptly, can help prevent overheating and prolong the life of the catalytic converter. Monitoring the engine temperature gauge and ensuring proper cooling system function are also crucial in preventing overheating-related catalytic converter failure.
4. Improper Fuel and Oil Usage
Using the wrong fuel or oil can also contribute to catalytic converter failure. Certain fuels, such as leaded gasoline, can damage the catalyst inside the converter, rendering it ineffective. Similarly, using oil that does not meet the manufacturer’s specifications or using too much oil can lead to increased emissions and potential damage to the catalytic converter.
It is important to use the appropriate fuel and oil as recommended by the vehicle manufacturer. Following the manufacturer’s guidelines for fuel and oil usage can help prevent unnecessary strain on the catalytic converter and ensure its proper functioning.
5. Exhaust System Leaks
Exhaust system leaks can also cause catalytic converters to go bad. Any leaks in the exhaust system before the catalytic converter can introduce extra oxygen into the system, disrupting the delicate balance of chemical reactions inside the converter. This can lead to increased emissions and reduced converter efficiency.
Regularly inspecting the exhaust system for leaks and promptly repairing any identified issues can help prevent further damage to the catalytic converter. Proper maintenance of the entire exhaust system, including the manifold, pipes, and muffler, is essential in ensuring the catalytic converter’s long-term performance.
These are just a few of the common reasons why catalytic converters can go bad. Understanding these causes and being vigilant about maintenance and repairs can help ensure the longevity and effectiveness of the catalytic converter, ultimately contributing to cleaner air and a healthier environment.
Frequently Asked Questions
In this section, we will address some common questions about how catalytic converters can go bad and what factors contribute to their failure.
1. How do catalytic converters go bad?
There are several ways in which catalytic converters can deteriorate and eventually fail. One common cause is contamination. Over time, the converter can become clogged or coated with pollutants, such as carbon deposits, oil residues, or unburned fuel. This buildup restricts the flow of exhaust gases, reducing the converter’s efficiency.
Another factor is thermal stress. The catalytic converter operates at high temperatures, and over time, this constant exposure to extreme heat can cause the catalyst materials to break down or become damaged. Additionally, physical damage, such as impacts from road debris or potholes, can also cause the converter to fail.
2. What are the symptoms of a failing catalytic converter?
When a catalytic converter starts to go bad, there are a few telltale signs to look out for. One common symptom is a decrease in engine performance. You may notice reduced power, sluggish acceleration, or difficulty maintaining speed. Another indicator is increased fuel consumption. A failing converter can cause the engine to run inefficiently, leading to higher fuel consumption.
Additionally, a failing catalytic converter can trigger the check engine light on your dashboard. This is because the converter is equipped with oxygen sensors that monitor its efficiency. If the sensors detect issues with the converter’s performance, they will send a signal to the engine control unit (ECU), which will illuminate the check engine light.
3. Can a catalytic converter fail due to poor maintenance?
Yes, poor maintenance can contribute to the failure of a catalytic converter. Regular maintenance, such as oil and filter changes, helps prevent contaminants from entering the exhaust system and damaging the converter. Neglecting regular maintenance can lead to increased levels of pollutants in the exhaust gases, accelerating the deterioration of the converter.
Furthermore, driving habits can also affect the lifespan of a catalytic converter. Frequent short trips or stop-and-go driving can prevent the converter from reaching its optimal operating temperature, leading to the buildup of deposits and premature failure. Therefore, proper maintenance and driving habits play a crucial role in the longevity of a catalytic converter.
4. Can a faulty catalytic converter harm the engine?
While a faulty catalytic converter won’t directly harm the engine, it can have indirect negative effects. A failing converter can lead to reduced engine performance, increased fuel consumption, and even engine misfires. These issues can put additional strain on the engine and its components, potentially leading to further damage if left unaddressed.
Furthermore, a failing catalytic converter can cause an increase in harmful emissions, as it may no longer effectively convert pollutants into less harmful substances. This can result in environmental damage and may lead to the vehicle failing emissions tests, which could result in fines or the inability to renew registration.
5. Can a catalytic converter be repaired or should it be replaced?
In most cases, a catalytic converter should be replaced rather than repaired. Once a converter has failed, it is difficult to restore its original function. Attempts to repair a damaged converter often yield temporary results or may even cause further damage. Therefore, it is generally recommended to replace a failed catalytic converter with a new or refurbished unit.
It is important to note that replacing a catalytic converter should be done by a qualified professional, as it involves working with the vehicle’s exhaust system and emissions components. They will ensure that the new converter is properly installed and meets the necessary specifications for your vehicle.
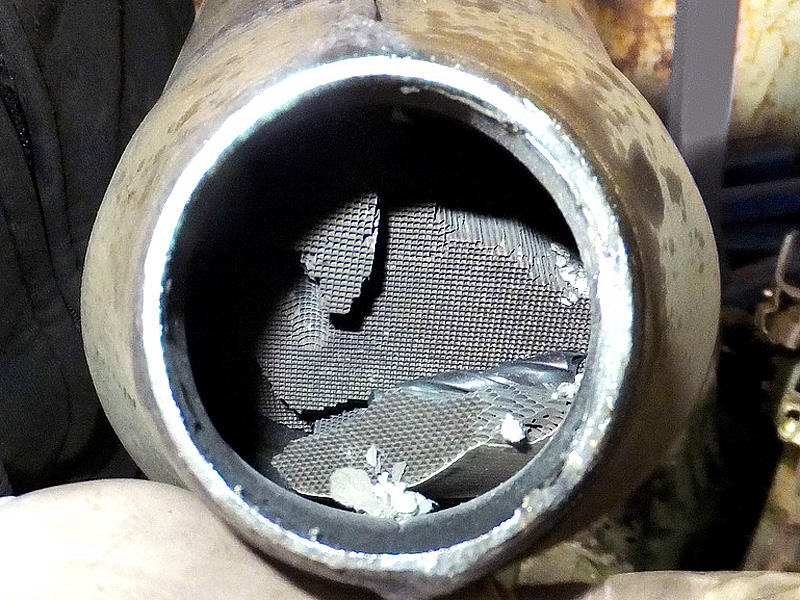

In conclusion, understanding the factors that can lead to the deterioration of catalytic converters is essential for drivers and automotive enthusiasts alike. By recognizing the various reasons behind their deterioration, individuals can take proactive measures to prevent premature failure and ensure the longevity of these crucial components.
From excessive heat and fuel additives to engine misfires and contamination, a catalytic converter can go bad due to a range of factors. Regular maintenance, such as checking for and promptly addressing any engine issues, can significantly extend the lifespan of this vital emission control device. Additionally, being mindful of driving habits, such as avoiding harsh acceleration and ensuring proper fuel quality, can help minimize the strain on the catalytic converter and mitigate the risk of it going bad.
Overall, staying informed about the potential causes of catalytic converter failure empowers vehicle owners to make informed decisions and take preventative actions. By doing so, we can not only protect the environment by reducing harmful emissions but also save ourselves from the inconvenience and expense associated with replacing a malfunctioning catalytic converter.
