In the world of automobiles, there are countless intricate systems working together to ensure smooth and efficient operation. One such system that often goes unnoticed, yet plays a vital role in enhancing performance and reducing environmental impact, is the exhaust system. While many drivers may simply view it as a pipe through which exhaust gases exit the vehicle, the exhaust system is actually a complex network of components that work harmoniously to achieve a multitude of objectives. From improving engine efficiency to reducing noise pollution, understanding how exhaust systems work is essential for any automotive enthusiast or aspiring mechanic.
At its core, the exhaust system serves the primary purpose of safely channeling and removing harmful emissions generated by the combustion process within the engine. However, its functions extend far beyond this basic responsibility. By carefully managing the flow of gases, the exhaust system helps optimize engine performance by ensuring proper backpressure, which in turn enhances fuel efficiency and power output. Additionally, it employs various components such as catalytic converters and mufflers to minimize harmful emissions and noise levels, respectively. Delving into the inner workings of this intricate system will unveil a fascinating world of engineering ingenuity that every car owner should appreciate.
How do exhaust systems work?
An exhaust system is responsible for removing waste gases from an engine and reducing noise. It consists of several components, including the exhaust manifold, catalytic converter, muffler, and tailpipe. As exhaust gases flow through the system, harmful pollutants are reduced, while noise is dampened. The system works by utilizing the principles of combustion and utilizing various components to redirect and filter the exhaust gases.
How Exhaust Systems Work
An exhaust system plays a vital role in the overall performance and efficiency of a vehicle. It is responsible for removing the harmful gases produced during the combustion process and reducing noise levels. Understanding how exhaust systems work can help you maintain and optimize your vehicle’s performance. In this article, we will provide a step-by-step guide on the functioning of exhaust systems.
1. Exhaust Manifold
The exhaust manifold is the first component of the exhaust system. It is directly connected to the engine’s cylinder head and collects the exhaust gases from each cylinder. The manifold’s primary function is to channel the gases into a single pipe. It is usually made of cast iron or stainless steel to withstand high temperatures.
Furthermore, the shape and design of the manifold are crucial for ensuring efficient flow of exhaust gases. A well-designed manifold can help improve engine performance by reducing back pressure and enhancing exhaust scavenging, which promotes better combustion.
2. Catalytic Converter
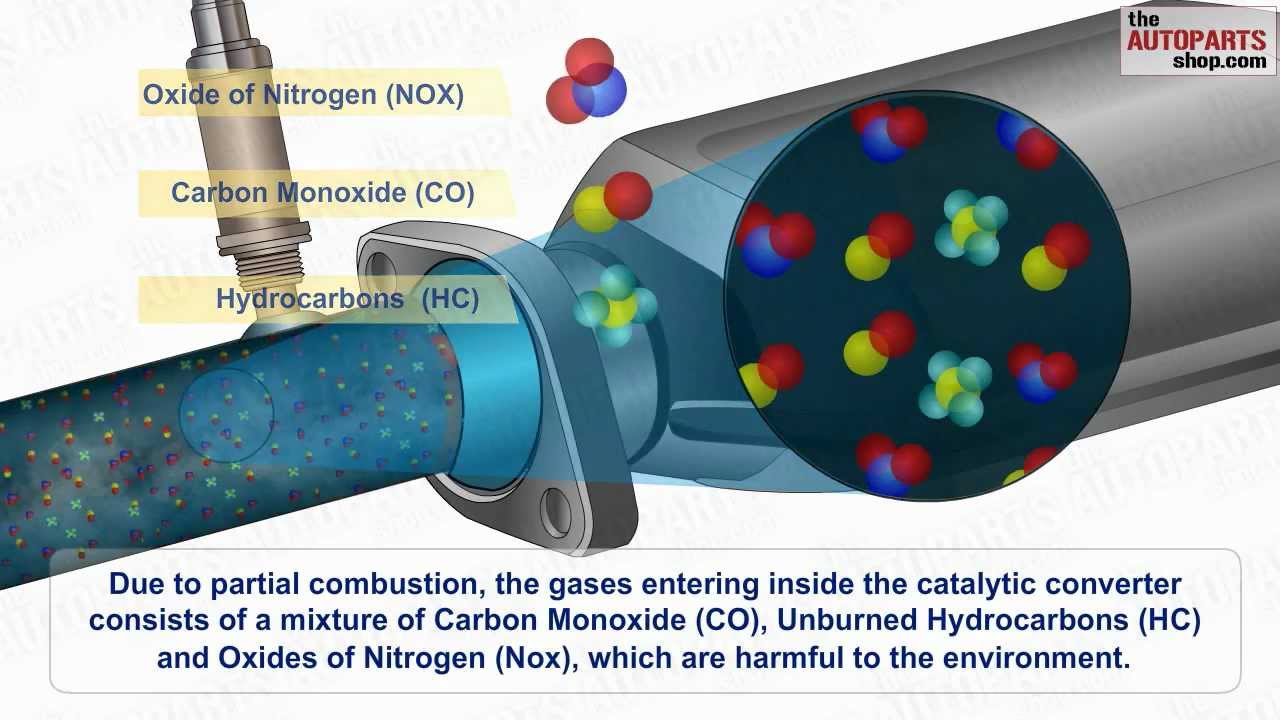
The catalytic converter is a crucial component of the exhaust system that helps reduce harmful emissions. It contains a catalyst, typically made of platinum, palladium, and rhodium, which facilitates chemical reactions to convert harmful gases into less harmful substances.
As the exhaust gases pass through the catalytic converter, the catalyst promotes oxidation of carbon monoxide (CO) into carbon dioxide (CO2) and reduction of nitrogen oxides (NOx) into nitrogen (N2) and oxygen (O2). It also helps convert unburned hydrocarbons (HC) into carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O). This process significantly reduces the emission of pollutants from the vehicle’s exhaust.
3. Muffler
The muffler, also known as a silencer, is responsible for reducing the noise produced by the exhaust gases. It consists of chambers and baffles that help attenuate the sound waves. When the exhaust gases pass through the muffler, the chambers and baffles disrupt the flow and create turbulence, which reduces the noise level.
Additionally, some mufflers also incorporate sound-absorbing materials such as fiberglass or steel wool. These materials help further dampen the sound waves by absorbing and dissipating the energy. As a result, the vehicle’s exhaust noise is significantly reduced, providing a quieter and more comfortable driving experience.
4. Tailpipe
The tailpipe is the final component of the exhaust system, responsible for expelling the treated exhaust gases out of the vehicle. It is usually located at the rear of the vehicle and is designed to direct the exhaust gases away from the vehicle’s body.
The tailpipe’s design may vary depending on the vehicle’s make and model. Some tailpipes may have a simple straight shape, while others may feature decorative tips or resonators to enhance the vehicle’s aesthetics or alter the exhaust sound.
5. Oxygen Sensors
Oxygen sensors, also known as O2 sensors, are essential components that monitor the oxygen content in the exhaust gases. They provide feedback to the engine control unit (ECU) to adjust the air-fuel mixture for optimal combustion efficiency.
The oxygen sensor measures the oxygen levels before and after the catalytic converter. Based on the readings, the ECU can make necessary adjustments to the fuel injection system, ensuring the engine operates within the desired parameters. This helps improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions.
6. Resonator
A resonator is an optional component that can be included in the exhaust system to modify the sound produced by the engine. It is typically placed after the catalytic converter and before the muffler. The resonator works by creating sound waves that cancel out or modify specific frequencies, resulting in a different exhaust note.
Resonators can be used to enhance the engine’s sound, creating a deeper or sportier tone. They can also be used to reduce specific frequencies that may cause undesirable resonances or drone inside the vehicle’s cabin. The inclusion of a resonator in the exhaust system allows for customization of the overall sound experience.
7. Exhaust Pipe
The exhaust pipe connects all the components of the exhaust system, allowing the smooth flow of exhaust gases from the engine to the tailpipe. It is typically made of stainless steel or aluminized steel to withstand high temperatures and resist corrosion.
The diameter and length of the exhaust pipe can affect the performance of the vehicle. A larger diameter pipe can help reduce back pressure and improve exhaust gas flow, resulting in better engine performance. Conversely, a smaller diameter pipe may increase back pressure and limit the engine’s efficiency.
8. Heat Shield
A heat shield is a protective component used to prevent excessive heat from reaching other parts of the vehicle. It is usually made of aluminum or stainless steel and is installed around the exhaust system components that are in close proximity to sensitive areas.
The heat shield helps minimize heat transfer to the vehicle’s body, wiring, fuel lines, and other heat-sensitive components. This prevents potential damage or malfunction caused by excessive heat. The heat shield also helps maintain a safe and comfortable temperature inside the vehicle’s cabin.
9. EGR Valve
The exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) valve is a device that controls the flow of exhaust gases back into the engine’s combustion chamber. It is primarily used in gasoline and diesel engines to reduce nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions.
By recirculating a portion of the exhaust gases, the EGR valve lowers the combustion temperature and reduces the formation of NOx. This helps vehicles comply with emission regulations while maintaining optimal engine performance.
10. Hangers and Clamps
Hangers and clamps are essential elements that secure and support the various components of the exhaust system. They ensure that the exhaust system remains in place and properly aligned, preventing excessive vibrations or movement that could lead to damage or failure.
Hangers are typically made of rubber or metal and are used to suspend the exhaust system from the vehicle’s chassis. They provide flexibility while also absorbing vibrations and shocks. Clamps, on the other hand, hold the different exhaust components together, ensuring a tight and leak-free connection.
Understanding how exhaust systems work is crucial for maintaining and optimizing your vehicle’s performance. By following the step-by-step guide provided in this article, you can gain valuable insights into the functioning of each component and make informed decisions regarding maintenance, upgrades, or customization of your vehicle’s exhaust system.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some commonly asked questions about how exhaust systems work. Take a look to learn more about this important automotive component.
Q: How does an exhaust system work?
An exhaust system works by removing waste gases produced by the engine during the combustion process. It starts with the exhaust manifold, which collects the gases from each cylinder and directs them into a single pipe. From there, the gases flow through the catalytic converter, which helps reduce harmful emissions. Next, they pass through the muffler, where noise is reduced, and finally exit through the tailpipe.
The exhaust system also plays a role in improving engine performance. By optimizing the flow of exhaust gases, it helps the engine breathe better, which can lead to increased power and fuel efficiency.
Q: What are the main components of an exhaust system?
The main components of an exhaust system include the exhaust manifold, catalytic converter, muffler, and tailpipe. The exhaust manifold collects the gases from each cylinder, while the catalytic converter helps reduce harmful emissions by converting them into less harmful substances. The muffler is responsible for reducing noise levels, and the tailpipe is the final exit point for the gases.
In addition to these components, some exhaust systems may also include resonators and flex pipes, which further refine the sound and flexibility of the system, respectively.
Q: How does a catalytic converter work?
A catalytic converter works by using a catalyst, typically made of platinum, palladium, and rhodium, to facilitate chemical reactions that transform harmful gases into less harmful ones. It contains a honeycomb-like structure coated with the catalyst, which provides a large surface area for the reactions to occur.
During operation, the catalytic converter facilitates the conversion of carbon monoxide (CO) into carbon dioxide (CO2), nitrogen oxides (NOx) into nitrogen (N2) and oxygen (O2), and unburned hydrocarbons (HC) into carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O).
Q: Why is the muffler important in an exhaust system?
The muffler is an important component of an exhaust system because it helps reduce noise levels produced by the engine. Inside the muffler, there are chambers and baffles designed to reflect and absorb sound waves, effectively muffling the noise produced during the combustion process.
In addition to reducing noise pollution, the muffler also helps improve engine performance. It does this by controlling backpressure, which is the resistance to the flow of exhaust gases. By optimizing backpressure, the muffler ensures that the engine can expel exhaust gases efficiently, leading to improved power and fuel efficiency.
Q: How can I maintain my exhaust system?
To maintain your exhaust system, it is important to regularly inspect it for any signs of damage or corrosion. Look for rust, holes, or loose connections. If you notice any issues, it is recommended to have them addressed by a qualified mechanic.
In addition to inspections, it is also important to keep your vehicle’s engine properly tuned. A poorly tuned engine can produce higher levels of harmful emissions, which can put additional strain on the exhaust system. Regular oil changes and using high-quality fuels can also help keep the exhaust system in good condition.
In conclusion, understanding how exhaust systems work is essential for every vehicle owner. By effectively removing harmful gases and reducing noise, exhaust systems play a crucial role in maintaining the performance and longevity of our cars. From the engine to the tailpipe, each component works together seamlessly to ensure the best possible driving experience.
Moreover, as technology continues to advance, exhaust systems are also evolving. From traditional mufflers to catalytic converters and diesel particulate filters, the industry is constantly finding new ways to reduce emissions and increase efficiency. It is important for us as consumers to stay informed about these advancements and make conscious choices that prioritize both our vehicles’ performance and the environment’s well-being.
In conclusion, by understanding how exhaust systems function and staying updated on the latest innovations, we can contribute to a cleaner and healthier future for ourselves and our planet. So, let us appreciate and take care of our exhaust systems, as they silently work to keep our engines running smoothly and our environment free from harmful pollutants.
- How to Close Spark Plug Gap: Expert Tips and Tricks! - May 13, 2024
- How to Perfectly Align Projector Headlights With Halo - May 13, 2024
- How Many Amps Does a Car Horn Draw? Unveiling the Power Requirements - May 13, 2024
